
The northern lights are an example of an aurora, and their proper scientific name is aurora borealis.
In pictures, they look like brightly coloured clouds and the colours can range from red, yellow-green to blue, and can cover large sections of the sky. The most spectacular thing, however, is that they move!
There are different types of aurorae, but the most well-known look like "curtains" of light, with ripples and curls moving along their lengths.

To understand why they are so brightly coloured, you can compare them to a television.
A television produces pictures by firing a beam of electrons at the back of the television screen that you watch. The screen glows different colours depending on the type of chemicals that coat the screen.
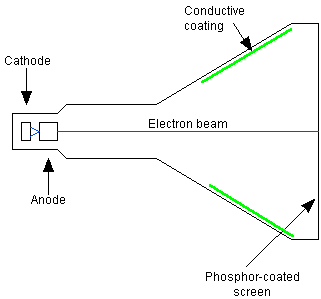
The aurorae come about by particles in the solar wind brushing past the Earth's magnetic field. The energy generated sends charged particles flying down into the Earth's atmosphere.
These particles act like the electron beam in your television set. The Earth's atmosphere is made up mainly of oxygen and nitrogen, and these act like the chemicals on the back of the TV screen, giving out brightly coloured light as the particles collide with them.

|