Q) What is electricity and how is it produced ?
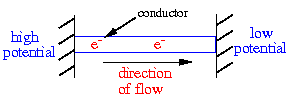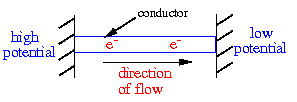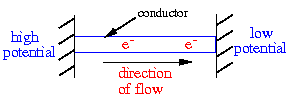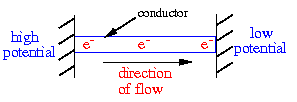
Electricity or an electrical current is a flow of electric charge
along a wire. The more charges that are passing
along the wire the larger the current. For the charges to flow along
the wire a force is needed to push them and this force is called the
voltage or potential difference. Charges will flow from regions of
high potential to regions of low potential where the potential difference
is the difference in potential of the two regions.
To get charges to flow from a region of high potential to a region of low
potential the two regions have to be connected with a conductor.

|
There are two types of electricity or electrical current that you will have come across. The first kind is called the direct current (dc) which comes from batteries and the second type is called the alternating current (ac) which comes out of plugs in the wall and is produced in power stations. The type of current that comes out of walls (ac) differs greatly from that which comes out of batteries (dc).
1) To begin with the ac electricity we come across is much more powerful than dc electricity. The voltage coming out of a wall is 240 V while that supplied from a battery is 1.5 V. This means that there is 160 times more pushing power acting on the electons in an ac current compared to a dc current.
2) Secondly in a direct current (dc) the electrons always flow in
the same direction but in an alternating current (ac) the current flows in one
direction and then another. In Britian the current changes direction
50 times a second.
 
|
Click here to find out more about alternating current (ac) electricity.
For electricity to flow objects called conductors are required. A conductor is an object that allows electrical charges to flow easily. Conductors are mainly metals. As well as having objects that conduct electricity there are objects that do not conduct electricity. These are called insulators, they allow very few electrical charges to flow.
Insulators : Plastics, Glass, Dry Air, Wood.



|